Department of Hospital Pediatric Surgery
The students of the 1st and 6th courses of TashPMI where the subject pediatric pediatric surgery and the basics of outpatient surgery are taught, which provides training of doctors for primary health care, are conducted at the department. In addition, the department trains clinical residents and residents of the magistracy in the specialty – pediatric surgery.
The educational process uses 80 video films, 5 manuals on CD-disks, about 120 slides, tools, the corresponding diagnostic and therapeutic equipment of the clinic.
In practical exercises, besides the above, video and computer technology is used, which significantly increases the visual informativeness of the practical lesson, allows demonstrating educational presentations and films.
Thanks to the initiative of prof. N.Sh. Ergasheva at the department organized a library, in the funds of which there are textbooks and monographs on children’s surgery, magazines. “Children’s surgery”, “Surgery”, “Herald of surgery”, “Pediatrics”, “Surgery of Uzbekistan”, etc. (total more than 100 titles). The library fund can be used by students both during the day and during the clinic’s stay.
All lectures are prepared and conducted in the form of multimedia presentations, it allows increasing the informative content of the presentation of the material.
Classes and lectures are held according to plan, the material is presented exclusively in Russian and Uzbek languages at a high methodological and scientific level.
The documentation on educational and methodical work is in proper condition.
On well-designed stands, the necessary information for students is provided in full on the schedule and topics of classes, lectures, consultations, workings, independent work, as well as scientific and practical achievements of employees.
Each teacher has a full set of methodological developments, structural and logical schemes of practical training in discipline, tests of the initial and final level, problematic clinical and situational tasks.
Thematic plans for lectures and practical classes have been approved in accordance with the new program, hours for independent work of students have been selected.
The list of compulsory practical skills is developed in accordance with the requirements of the qualification characteristics of the doctor-child surgeon.
Assessment of students’ knowledge is carried out according to the rating system. The final exams are conducted by the test control method in the test center of TashPMI.
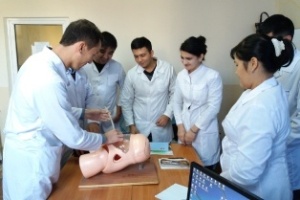

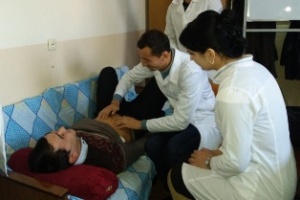
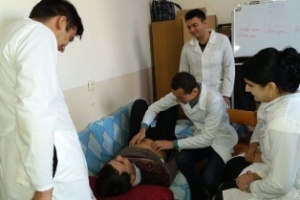
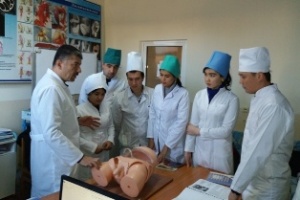
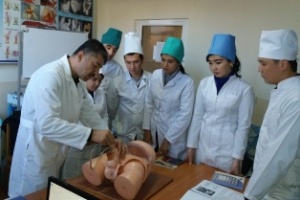
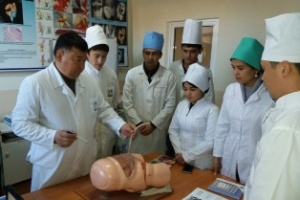


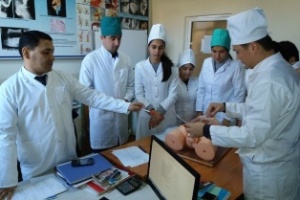


Students of VI course held at the hospital. In studying the subject of Hospital Pediatric Surgery students based on knowledge obtained by 4-5 courses. At 6 course focuses on the differential diagnosis allocated surgical diseases, atypical and complicated course of the disease, the choice of the optimal diagnostic and therapeutic measures for complications of surgical diseases, and prevention and clinical examination in the primary care setting.
Objectives:
Prepare a general practitioner pediatrician for independent management of qualified medical and preventive work in primary health care, the provision of diagnostic and medical care in emergency situations for emergency care, the provision of diagnostic and medical home care, day hospital, outpatient clinics in the most common surgical diseases children at different stages of their course, the implementation of sanitary, epidemiological and preventive measures in the centers of mass destruction, rehabilitation after discharge from hospital.
Tasks:
- Organization of the educational process of the single courses students (training of general practitioners pediatrician), integrated with the basic biomedical disciplines, given the practical skills needed for the job.
- The deepening of the integration of knowledge and skills acquired during the previous study.
- Developing skills of independent work in all phases of general practitioner pediatrician carried out in accordance with the regimentation of qualifying characteristics. Requirements for knowledge, skills and abilities of students the student should know:
- Etiopathogenic basis of surgical diseases of childhood.
- Clinical presentations of surgical pathology in childhood, clinical and differential diagnosis.
- Clinical features of normal and complicated surgical diseases, depending on the age and premorbid background.
- Diagnostic value of individual symptoms and syndromes.
- Instrumental methods, biochemical, serological, morphological studies.
Their capabilities and applications.
- General principles of surgical treatment of diseases of children.
- Methods of clinical examination and rehabilitation of children with surgical diseases.
- Mastering the principles of the organization of surgical care for children’s population in primary care.
- Familiarization with small surgical procedures and operations. the student should be able to:
- Collect medical history and examine the patient to identify the surgical pathology.
- Identify criteria for early diagnosis, depending on the characteristics of the disease, to make a differential diagnosis.
- Formulate a diagnosis using the classifications of the disease and to determine the treatment strategy.
- Interpret the results of functional, instrumental and laboratory studies.
- Make a plan and posindromnoy pathogenetic therapy.
- Identify indications and expert advice.
- It makes the rehabilitation regimes.
- To provide emergency assistance in emergency situations.
- Be able to perform minor surgical procedures, and operations.
1 course
The purpose of teaching science is to create knowledge and skills to ensure the quality of medical care needed to improve the health of adults and children.
Objectives of the subject:
– training in the rules of care for adults, children and adolescents in the provision of inpatient medical care;
– training in the rules of the regime in medical institutions;
– familiarization with the principles of deontology and ethics;
– training in the rules of sanitary treatment of adults and children in the hospital during treatment;
– familiarization with the concepts of anthropology and thermometry;
– Training in the care of patients with the most common diseases in treatment;
– training in the rules of nutrition and feeding patients, depending on the type and severity of the disease, as well as the age of the patient;
– learning the rules of admission and ways of taking medicines;
– training in the implementation of medical procedures;
– training in the rules for preparing patients for emergency and planned operations;
– training in the care of patients who are in the intensive care unit and after transferring them to the surgical department;
– training in the rules of first aid to patients with life threatening conditions (heart failure, breathing disorder, bleeding, poisoning, burns, frostbite, aspiration);
– training in the collection of biological materials for laboratory tests;
– training in the rules of using scientific literature on modern methods of caring for patients.
Requirements for the knowledge, skills and qualifications of students on the subject.
Student:
should have an idea of:
– the principles of deontology in the care of patients;
– types of treatment and prevention institutions;
– the meaning and rules of care for patients;
– medical documents and the order of their management;
– rules for the storage and dispensing of medicinal products;
– rules for disinfection, sterilization, asepsis and antiseptics;
– rules of personal hygiene of personnel.
know and be able to apply:
– physiological and therapeutic tables,
– rules for feeding patients and handling dishes;
– mode of motion;
– indications for the use of resuscitation, the concept of “resuscitation”, “clinical death”, “biological death”;
– types of patient sanitation;
– Preparation of patients for X-ray, ultrasound and other studies.
Possess practical (clinical) skills:
– cleaning of premises, ventilation of premises, current and final disinfection;
– rules and methods of drug administration;
– medical procedures (thermometry, anthropometry, measurement of respiratory rate and heart rate, measurement of blood pressure);
– Carrying out of medical procedures (inhalations, use of mustard plasters, etc.);
– methods of immobilization of various parts of the body;
– Care for the sick.
Department of Oncology with Pediatric Oncology.
The course is attended by students of the V-VI courses of the medical-pedagogical faculty, the sixth year of pediatric faculty, and the third year of higher nursing. In addition, on the course are trained and clinical residents in the specialty – oncology.
In teaching, along with traditional methods (posters, color slides, training radiographs, etc.) use modern technical means of teaching – video lectures, video fragments of complicated operations, electronic textbooks.
Assessment of students’ knowledge is carried out according to the rating system. Final examinations are conducted by oral control on the basis of the course.
III-course – higher nursing, V-VI course, medical-pedagogical faculty, VI course-pediatric faculty.
The present program on oncology determines the amount of theoretical knowledge and practical skills that a student must master when training on an oncology course. This program is designed for students of medical schools, taking into account the main practical tasks facing future general practitioners. Methodical guidance and coordination of teaching are carried out by the managers of the course of oncology.


Goal:
The goal of oncology training is the acquisition by the student of the knowledge, skills and practical skills necessary for the subsequent professional activity as a general practitioner.
Tasks:
- Acquaintance with the peculiarities of the organization of oncological care for the population of Uzbekistan and modern principles of treatment of cancer patients.
- Training the future general practitioner tactics in case of suspected malignant neoplasm in the patient.
- To deepen the practical training of a general practitioner in the prevention, early diagnosis of malignant tumors.
- Training of a general practitioner for secondary cancer prevention, early diagnosis of cancer and tactics of oncological patients after treatment in a specialized institution.
- Prepare for methodical help in planning practical preventive measures.
- Mastering the methods of palliative care for cancer patients in the far-advanced stage of the tumor process.
- Requirements for knowledge, skills and skills.
The student should know:
- Basic principles of ethics and deontology in oncology;
- The purpose and objectives of oncology, its importance for the activities of a general practitioner;
- Factors contributing to the development of malignant tumors and cancer prevention measures;
- Modern principles and results of radical, palliative and symptomatic treatment of malignant neoplasms;
- Clinical and morphological concepts of precancerous diseases;
- General principles of early diagnosis of malignant neoplasms in clinical syndromes;
- General principles of the basic methods of laboratory and instrumental diagnostics of malignant neoplasms and the principles of clinical evaluation of the results of these studies.
The student should be able to:
- Descriptions of the cancer status in the medical documentation;
- Directions of an oncological patient to a specialist;
- Conducting a conversation and questioning with oncological patients and their relatives;
- Palpation of tumor formation in various organs (mammary gland, abdominal and pelvic organs, soft tissues);
- Palpation of peripheral lymph nodes to identify metastatic lesions;
- Mastering the technique of smear and puncture biopsy;
- Mastering the technique of catheterization of the bladder;
- Mastering the technique of colostomy care;
- Mastering all types of cleansing and treatment enemas;
- Mastering the technique of sensing and washing the stomach;
- Mastering the technique of digital rectal examination;
- Mastering the technique of examining female genital organs.
Test assignment on hospital pediatric surgery for the 7 course
Educational technology for students 6 Course
Questions intermediate control for students 6 Course
Educational texnology in the discipline “Hospital Pediatric Surgery” 6 course
Educational texnology in the discipline “Hospital Pediatric Surgery” 7 course
Educational texnology in the discipline “Hospital Pediatric Surgery” 6 course pediatric