

National Emblem of Uzbekistan
The national emblem of the Republic of Uzbekistan reflects the history, high spirituality, eternal values and way of life of Uzbek people. Each element, color and sign of the emblem has its own symbolic meaning. The emblem is set off by a garland of cotton branches with open cotton bolls and ears of wheat. Wheatears are the symbol of the daily bread; stems with open cotton bolls are the main wealth of the sunny land, which have glorified it throughout the world. Stems and cotton bolls, tangled with a ribbon of the state flag, represent the solidarity of the peoples living in the republic. There is the sun depicted on the emblem, the golden rays of which are piercing through the blossoming valley. The representation of the sun is the wish that the way of the state has always been lit up with a glare. At the same time, the sun reflects the unique natural and climatic conditions of the republic. Rivers flowing down from the mountains symbolize a sanguineous life. Inside the octagon, placed in the top of the emblem and embodying the freedom and unity of the people, there is a crescent and stars, shining against the background of the blue sky. This is a symbol of eternity, national traditions and values, high spirituality, strength of will and faith. Humo bird with extended wings, located in the center of the emblem, has long been considered a symbol of fidelity and love of freedom. Great Uzbek poet, Alisher Navoi characterized Humo bird as the kindest of all living beings. There is an inscription "Uzbekistan" at the bottom of the emblem, drawn on the base of the garland of the state flag with golden letters. The State Emblem of the Republic of Uzbekistan was approved on July 2, 1992 at the tenth session of the Supreme Council of the Republic of Uzbekistan.

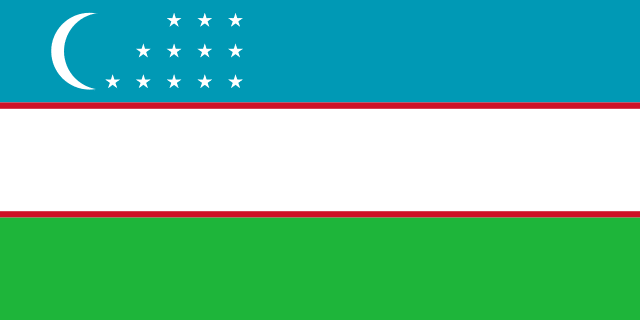
National Flag of Uzbekistan
The state flag of Uzbekistan was approved on November 18, 1991 and since then, it is an official national symbol of the republic. It represents a multicolored rectangular cloth with three horizontal stripes of blue, white and green. Everything on Uzbek flag is symbolic and reflects the perception of the world of the Uzbek people and has a connection with their historical and cultural past. The blue stripe on the flag is the symbol of the sky, water, and traditional symbol of peace, as well as the sign of historical continuity (the flag of Amir Temur’s state was also blue in color). The white line on the cloth is the color of peace in perception of the Uzbek people, which is reflected even in the ordinary Uzbek expression "ok yul!", which means, "go in peace!". The green color on the banner is the color of nature, new life and abundance in countries where the majority of is population are Muslims. Red lines - symbolize the vital energy, New half moon - reflects both the national independence of the republic, and connection with the historical past of the people, its traditions. On the banner, 12 stars are also depicted, symbolizing twelve regions of the country as well as ancient solar calendar.
National Anthem
The law "On national anthem of the Republic of Uzbekistan" was adopted on the December 10, 1992 at the 11th session of the Supreme Council of Uzbekistan.
Poem by A. Aripov
Music by M. Burkhanov
My country, sunny and free, salvation to your people,
You are a warmhearted companion to the friends
Flourish eternally with knowledge and invention,
May your fame shine as long as the world exists!
Refrain:
These golden valleys-dear Uzbekistan,
Manly spirit of ancestors is companion to you!
When the great power of people became exuberant
You are the country that amazes the world!
Belief of generous Uzbek does not die out,
Free, young children are a strong wing for you!
The torch of independence, guardian of peace,
Just motherland be eternally prosperous!
Refrain:
These golden valleys-dear Uzbekistan,
Manly spirit of ancestors is companion to you!
When the great power of people became exuberant
You are the country that amazes the world!